Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City)
THE GIFT CITY VISION
With a vision of becoming a leading global financial & technology hub, the evolution of GIFT City is an opportunity to drive reforms toward providing a thriving financial ecosystem critical to supporting and expanding businesses. GIFT City is inclined to provide a conducive business ecosystem at par or above with leading global financial hubs. GIFT City is a project of national importance and has become an integral part of India’s growth story as the country marches towards realizing the dream of becoming a developed nation.
Gujarat: A Hub of Opportunities
Gujarat's strategic location, robust infrastructure, and proactive governance have made it a preferred destination for businesses across the globe. The state boasts of a strong industrial base, encompassing sectors such as manufacturing, textiles, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture.
Moreover, Gujarat's entrepreneurial spirit has led to the emergence of numerous startups and SMEs, contributing significantly to innovation and job creation. With favorable policies, investment incentives, and a skilled workforce, the state continues to attract domestic and foreign investors alike.
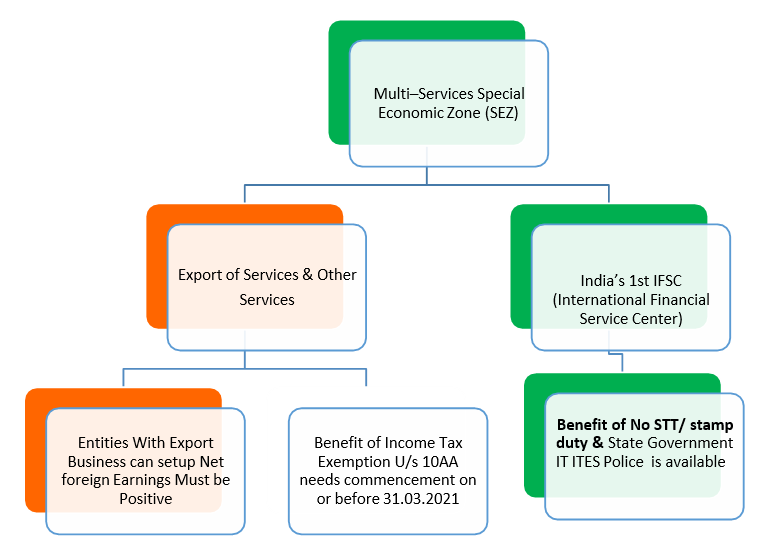
Gift City is majorly divided into three categories:
- DTA: Domestic Tariff Area means the whole of India (including the territorial waters and continental shelf) but does not include the areas of the Special Economic Zones.
- SEZ Area: A special economic zone (SEZ) is an area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country's national borders. Their aims include increased trade balance, employment, increased investment, job creation, and effective administration.
- IFSCA: The International Financial Services Centers Authority (IFSCA) was established by the Government of India to develop and regulate international financial services centers in the country.
GIFT CITY
Export Business, which can be Setup at SEZ:
- Audio-visual services, construction and related services
- IT & ITES
- Educational services, environmental services, hospital services, other human health services Engineering and design, graphic information system services
- Entertainment services
- Human resources services, insurance claim processing
- Legal databases, medical transcription remote maintenance Professional services rental/leasing
- services without operators
- Research and development services Support centers and website services
- Tourism and travel-related services, recreational, cultural, and sporting services
- Trading: (Import For Re-export)
- Warehouse services, services auxiliary all modes of transport, pipeline transport.
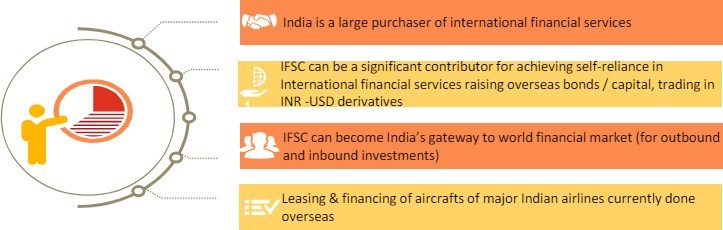
IFSC & Government of India’s vision for GIFT City
IFSC:
- An IFSC caters to customers outside the jurisdiction of the domestic economy. Such centers deal with the flow of finance, financial products, and services across the borders.
- IFSC as envisaged under the Indian context “is a jurisdiction that provides financial services to non- residents and residents (Institutions), in any currency other than Indian Rupee (INR)”
- IFSC is set up to undertake financial services transactions that are currently carried on outside India by overseas financial institutions and overseas branches/ subsidiaries of Indian financial institutions
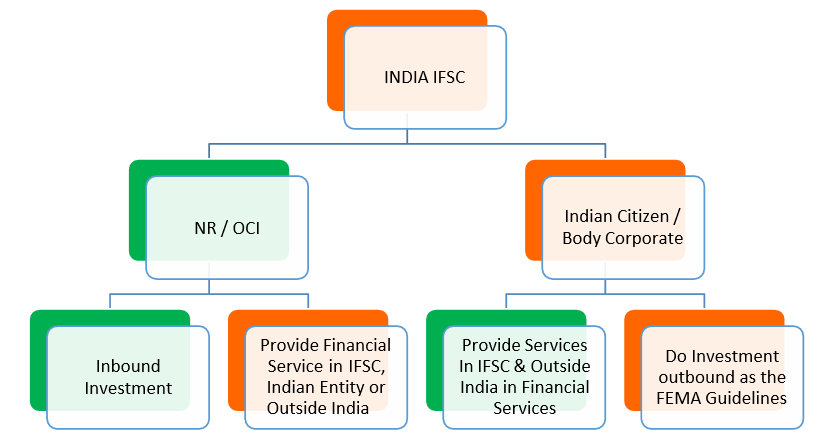
IFSC in India:
- In India, an IFSC is approved and regulated by the Government of India under the Special Economic Zones Act, of 2005
- The government of India has approved GIFT City as a Multi Services Special Economic Zone (‘GIFT SEZ’) and has also notified this zone as India’s IFSC
- The launch of the IFSC at GIFT City is the first step towards bringing financial services transactions relatable to India, back to Indian shores
- IFSC unit is treated as a non-resident under extant Foreign Exchange Management Regulations.
GET IN TOUCH WITH US
Always ready to help you out regarding all your queries.

Potential for IFSCA
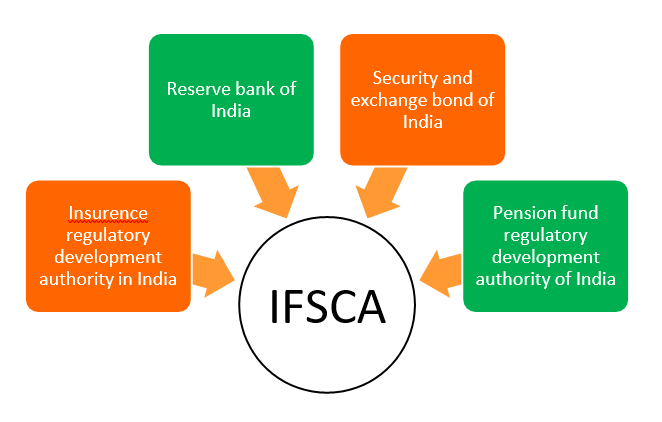
Regulatory powers of four financial services regulators in India vested in the IFSCA concerning the regulation of financial institutions, financial services, and financial products in the IFSC, making it a unified regulator for the IFSC.
Business in Gift IFSCA
In IFSC Financial Service Means
- Buying, Selling, or Subscribing to Financial Products
- Acceptance of Deposits
- Safeguarding and Administering Assets
- Effecting Contracts of Insurance
- Offering, Managing, or Agreed Asset Management
- Exercising Rights Associated with Financial Products
- Establishing or Operating Investment Schemes
- Maintaining or Transferring Records of Ownership
- Underwriting Issuance or Subscription of Financial Products
- Providing Information about Financial Standing or Creditworthiness
- Issuing Stored Value or Payment Instruments
- Arranging Services in the Above Categories
- Rendering Advice on Financial Products or Services
- Book-keeping, Accounting, Taxation, and Financial Crime Compliance Services
IFSC Capital Market
- Stock Exchanges
- Brokers dealers
- Custodian, Depositories, Depositories Participants
- Clearing Corporation
- Underwriter, Custodian
- Investment banker, Advisors
- Account Aggregator
- Debenture trustee
- Wealth manager, Trusteeships service
Fund management entities
- Authorized FME
- NON-Retail FME
- Retail FME
- Venture capital
- REITS/INVITES
- PMS
- Family Investments funds
- Credit Exchange
- ETFs special funds
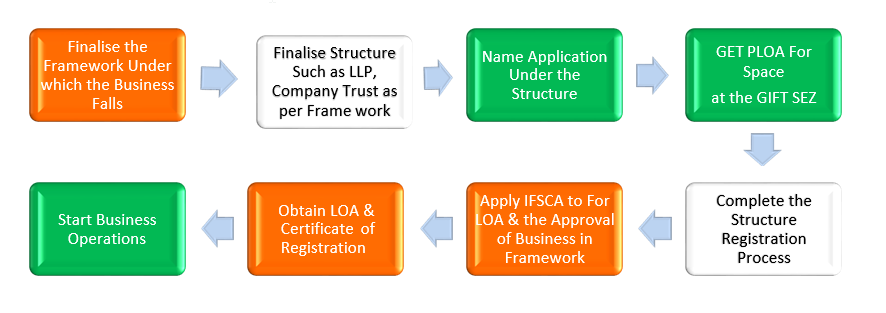
REGISTRATION PROCESS IN GIFT IFSCA
Tax Framework for IFSC
| Particular | Unit in IFSC | Investors |
|---|---|---|
| Income Tax |
|
|
| Goods & Services Tax | No GST on services – ✓ received by the unit in IFSC ✓ provided to IFSC / SEZ units or Offshore clients GST applicable on services provided to DTA |
No GST on transactions carried out in IFSC exchanges |
| Other Tax duties | State Subsidies – Lease rental, PF contribution, electricity charges | Exemption from STT, CTT, stamp duty in respect of transactions carried out on IFSC exchanges |
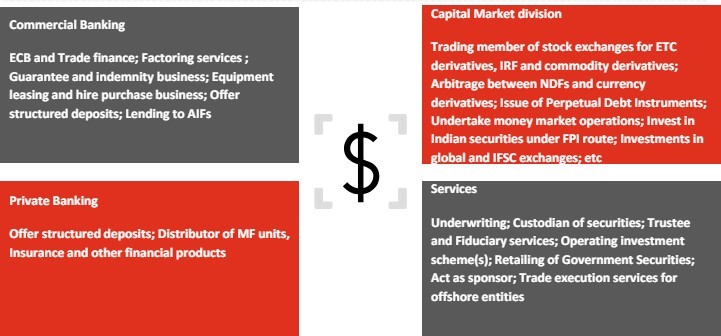
IFSC Banking
- IFSCA (Banking) Regulations, 2020 notified by IFSCA
- The new IFSCA regulation supersedes the earlier RBI IBU guideline.
Eligibility and Permissible Activities
- Indian and Foreign banks can set up an IBU as a branch – Indian Bank includes any bank formed under any Act and a subsidiary of a foreign bank incorporated in India but excludes co-operative banks
- Foreign banks not having a presence in India may also be permitted to set up an IBU
- Parent bank to satisfy the following conditions: ‒ Provide necessary capital to the IBU, subject to a minimum capital of US$20 million or as specified by IFSCA, which shall be maintained at the parent bank in the manner specified by IFSCA ‒ Obtain No Objection letter from its home regulator for setting up IBU in IFSC ‒ Submit an undertaking to provide liquidity to IBU, whenever needed.
- IFSCA Banking Regulations were recently liberalized to enable IBUs to provide wide spectrum activities now aligned with those permitted under the RBI Banking Regulations Act, 1949.
Tax regime for IBU’s in IFSC
- 100% tax exemption for any 10 consecutive years out of the first 15 years at IBU’s choice
- Tax regime for the investment division of an OBU, where OBU commences operations before 31 March 2024 to be as follows:
| Nature of income | Proposed income-tax rate (excluding surcharge and cess) |
|---|---|
| Capital gains on equity shares | 10% for LTCG, 15% / 30% for STCG |
| Capital gains on debt/ derivatives/offshore securities | Exempt |
| Dividends and interest income (except for interest under section 194LD) | 10% |
| Business income from a securitization trust | Exempt |
| Income from offshore securities | Exempt |
- Income of non-resident on the transfer of Non-Deliverable Forward (‘NDF’) contracts entered with IBU - exempt from tax, provided IBU commences operations before 31 March 2024.


